A Doctor Breaks Down What Happens to Your Body After Three Days Without Food
Last updated on
America faces a growing health crisis. Nearly 40 percent of the population now qualifies as obese, while obesity-related cancer deaths have tripled between 1999 and 2020. Fast food, processed meats, sugary drinks, and fried products dominate the national diet, earning the United States a reputation for having one of the worst eating patterns globally. But what if the solution didn’t involve eating at all? Dr. Eric Berg has spent years studying how the body responds when deprived of food. His research points to a counterintuitive finding that challenges conventional wisdom about healing and nourishment. According to the physician, Americans have been conditioned to believe that constant eating keeps us healthy. Yet he argues the opposite may be true. Going without food for 72 hours triggers a cascade of biological changes that begin within hours and accelerate dramatically by the third day. From cellular cleanup to immune system regeneration, the human body transforms itself when freed from constant digestion. Here’s what happens, hour by hour, when you stop eating for three full daysOne Hormone Controls Everything
Dr. Berg identifies a single culprit behind most chronic diseases. “There’s one single problem behind all chronic disease, including cancer, and that is insulin resistance,” he explains. Eating too frequently keeps insulin elevated, blocking the body’s natural repair mechanisms. Insulin resistance occurs when cells stop responding properly to insulin signals. Excess body weight and high-carbohydrate diets often trigger this condition, paving the way for metabolic imbalances and heart disease. Fasting reverses this pattern by keeping insulin levels steady, allowing cells to regain their sensitivity. Research published in JAMA Internal Medicine confirms these effects. Extended fasting protocols produce significant weight loss and improve cardiometabolic risk factors, including insulin sensitivity and blood pressure. Blood sugar regulation improves as the body learns to function without constant glucose influx.Your Body Starts Burning Different Fuel

Water Weight Drops Fast
Glycogen depletion accelerates as fasting continues. Liver stores of this stored sugar form begin running low. As glycogen breaks down, it releases the water molecules bound to it. Dr. Berg compares this process to squeezing water from a sponge. Rapid water weight loss occurs during this phase. Several pounds may disappear from the scale, though fat loss remains modest. Understanding this distinction prevents disappointment when weight loss appears to plateau after the first day. Ketone production ramps up as glycogen diminishes. Fatty acids get converted into these organic compounds, which serve as an alternative fuel source when glucose becomes scarce. Ketones can power nearly every cell in the body, from muscles to brain tissue. Energy levels may fluctuate during this metabolic transition. Some people feel tired as their bodies switch fuel sources, while others notice sustained energy without the usual post-meal crashes. Individual responses vary based on metabolic flexibility and prior eating patterns.Fat Becomes Your Primary Energy Source

Your Cells Start Eating Themselves
Around the 48 to 72-hour window, autophagy kicks into high gear. During this cellular cleanup process, the body identifies damaged or dysfunctional cells and breaks them down for parts. Useful components get recycled into new cells, while waste products get eliminated. Autophagy cannot occur when you constantly supply your body with food. Eating triggers insulin release, which shuts down this critical maintenance system. Only during extended fasting can cells fully engage their self-cleaning mechanisms. Cellular organelles, proteins, and other structures accumulate damage over time through normal wear and tear. Autophagy removes these compromised components, reducing cellular stress and improving overall function. Toxins and metabolic waste products that build up in cells also get cleared during this process.Your Immune System Gets a Complete Reset
Something Worth $50,000 Happens for Free
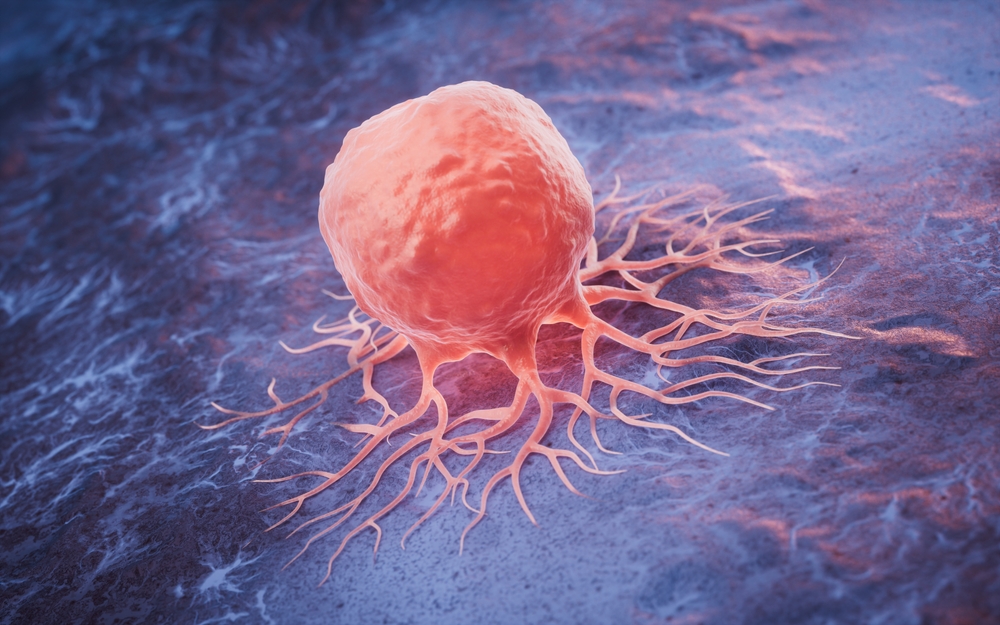
Stem cell production increases dramatically after three days without food. Dr. Berg notes the irony in this finding. “Some stem cell therapy is like $50,000, but guess what? You can get stem cell therapy, for free, by just not eating,” he states. Stem cells repair damaged tissues and generate new cells throughout the body. Enhanced stem cell production during fasting may contribute to the observed anti-aging effects and improved longevity. Cellular regeneration accelerates, potentially slowing the aging process at the molecular level. A study published in Cell Metabolism investigated prolonged fasting on cellular function and overall health. Researchers concluded that “fasting has the potential to delay aging and help prevent diseases while minimizing the side effects caused by chronic dietary interventions.”How to Actually Pull It Off
When Fasting Can Backfire

Not a Magic Bullet
Extended fasting produces measurable changes across multiple body systems. From insulin sensitivity to immune function, three days without food triggers biological responses that support health in ways conventional eating patterns cannot match. Yet fasting isn’t a magic cure-all. Individual responses vary based on metabolic health, age, activity level, and genetic factors. What works remarkably well for one person may produce minimal benefits for another. Current research suggests that extended fasting offers significant promise for metabolic health, cellular repair, and immune function. However, scientists continue investigating long-term effects and optimal fasting protocols. Medical guidance remains essential, particularly for people with existing health conditions. For those who can safely attempt it, a 72-hour fast provides a window into the body’s remarkable capacity for self-repair and regeneration. Perhaps the most powerful medicine doesn’t come from eating more, but from occasionally eating nothing at all.Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.
































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Comments