Essential Fatty Acids—All You Need To Know To Obtain Optimal Health
Last updated on
Along with carbohydrates, protein, water, vitamins and minerals, fats are one of the 6 groups of essential nutrients for the human body. Yet many people avoid essential fatty acids and try to cut them out of their diet completely, causing a host of unnecessary health problems.
Understanding fatty acids, and knowledge of how the body uses them will help you make the right decisions regarding your health.
Here is an easy-to-understand guide to essential fatty acids, the health benefits as well as some good dietary sources.
What Are Fatty Acids?
Similar to how amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, fatty acids are the building blocks of fats. The fat we eat gets broken down in the gut into fatty acids, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body.
We use the terms fats and fatty acids interchangeably in this article.
There are many fatty acids produced in the body. They can be saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated. Fatty acids can be broken into two groups—essential and non-essential fatty acids. Lets take a look at both.
What Are Essential Fatty Acids?
Essential fatty acids is the scientific term for fats that the body cannot make on its own. Linoleic Acid and Alpha-linolenic Acid are the only two essential fatty acids—they cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from our diet. The body can synthesize all other specialized fats including cholesterol, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from these two.
What Are The Non-Essential Fatty Acids?
Below are some of the better known non-essential fatty acids important for health. Non-essential means that they can be produced by the body, using the essential fats that you eat from food.
OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS
Omega-3 fatty acids are a family of unsaturated fatty acids that includes alpha-linolenic (though this is an EFA), eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). You may have seen these acronyms being used to market milk powder, although they are not the best sources of these fatty acids.
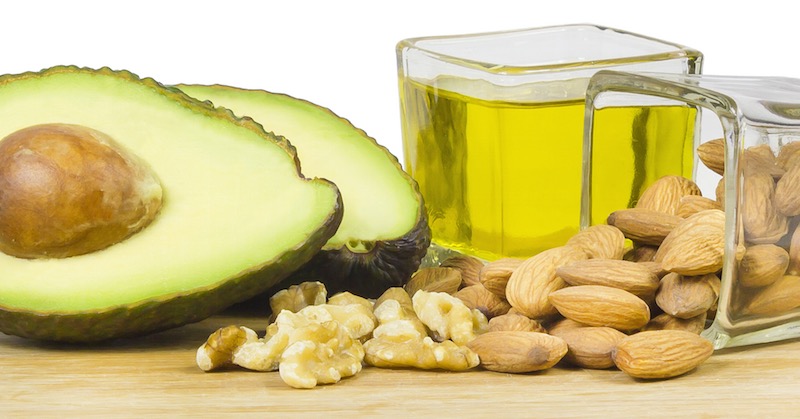
There are many excellent sources of omega-3 including seeds (chia, flaxseed, hemp); nuts (notably walnuts), avocado, and fish oils (such as cod liver, fresh salmon, herring, tuna and mackerel).
However, fatty acids are very sensitive to heat, and gets destroyed when cooked. Consequently you may not get much omega-3 from cooked fish as most are removed or destroyed.
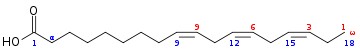
Omega-3 are named such because of their molecular structure which signifies that the first double-bond exists as the third carbon-carbon bond from the terminal methyl end of the carbon chain.
OMEGA-6 FATTY ACIDS
Omega-6 fatty acids are another family of the unsaturated fatty acid, which includes linoleic acid (though this is an EFA) and arachidonic acid – a precursor for making prostaglandins. They have a carbon-carbon double bond in the sixth position from the end of the fatty acid. Notice the molecular structure compared to that of omega-3.
What About The Bad, Unhealthy Fats?
There are several types of bad fat identified as potentially harmful to your health: saturated fat (often derived from animals); refined vegetable oils where the processing removes most of the original benefits, and trans fat.
Saturated and trans fat should be avoided or eaten sparingly.
The Role Of Fats In The Body
Fats play a key role in keeping the body working. Fats act as a backup source of energy when carbohydrates are unavailable, they insulate us, store fat-soluble vitamins, facilitate nerve transmissions, protect our vital organs and keep our heart, kidney and digestive system healthy.
- Fatty acids are vital for the membranes around every cell in our body, including our skin, hair and nails. It can help eliminate skin problems like dandruff, eczema, psoriasis, severe acne and brittle nails.
- EFAs can lower triglycerides (a fat in the blood) and increase HDL (good cholesterol).
- Together with our body’s natural cholesterol and protein, EFAs work to repair and construct new membranes thus reducing the effects of degeneration.
- Essential fatty acids increase the body’s metabolism in burning fats. So continuous consumption of EFAs actually helps you to lose weight!
- Effective for brain development and neural health.
- Essential fatty acids help lower blood pressure by eradicating plaques from the walls of arteries, preventing atherosclerosis.
- Reduces aggravation of inflammation from conditions such as arthritis, lupus, gout, and other inflammatory problems.
- EFAs also keep blood platelets from being sticky and clumping up thus allowing correct healing of wounds and preventing blood clots.
- EFAs assist in regulating the body’s cholesterol level and get rid of excess cholesterol from the blood.
- Fatty acids help the body manufacture hemoglobin, essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body. The EFAs are also able to hold oxygen that will help build the body’s defence system, increase metabolic efficiency and convert energy.
- Fatty acids shorten recovery time for tired muscles.
- Fatty acids help regulate body temperature.
- EFAs help make prostaglandins which regulate the immune system, which in turn can alleviate allergy symptoms.
Are you starting to see why fats are vital to the proper functioning of our body? Now let’s look at the symptoms of fatty acid deficiency.
Symptoms Of Fatty Acid Deficiency
An imbalance of essential fatty acids in the diet can cause many unwanted ailments and symptoms. Research has found that administering daily EFAs in their purest form helps treat:
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Gall bladder dysfunction
- Heart disease
- Infertility
- Kidney problems
- Lupus
- Mental issues such as impaired learning, behavioral and personality changes, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and depression
- Miscarriage
- Muscle tremors and impaired motor coordination
- Painful menstruation
- Poor physical growth
- Poor vision
- Skin disorders such as acne eczema, psoriasis.
- Slow healing of wounds
- Thirst due to excessive perspiration
Dosage And EFA Optimization
The body requires a balanced intake of omega-3 and omega-6. A high ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 results in harmful prostaglandins being produced in excess which can cause development of many illnesses. Ignorance to this fact means that the modern day diet often contains as much as 25 parts omega-6 to 1 part omega 3 (25:1) which is too high.
Taking EFAs in a balanced ratio by itself can help improve health in many ways. The presence of certain co-factors can help give EFA metabolism the extra boost and work synergistically in a very powerful way. These important co-factors are vitamin B6, A, C and E; and minerals copper, magnesium, selenium and zinc.
It is no coincidence that foods naturally rich in EFAs are also rich in these other minerals and nutrients. Examples are: beans, nuts, seeds and seafood. Taken with vitamins A and C from fresh vegetables (juice is better), this nutrient group is complete and can build strong immunity.
In order for your EFAs to work more effectively, you need also to eliminate harmful acid-forming foods from your diet:
- Milk and dairy products rob zinc and calcium from the body
- Trans-fat and saturated fats interferes with enzyme activities
- Excessive sugar intake increases copper deficiency and leaches magnesium which are then excreted in the urine. These are symptoms that your body is overloaded with sugar
- Refined salt constantly depletes magnesium and potassium from the body. Consider using these healthy alternative rock or sea salts
- Phosphate is an essential mineral, but large amounts from processed food causes the digestive tract to be sluggish, inhibiting the absorption of vitamins and minerals
- Pesticides interfere with the body’s ability to use vitamin B6
- Free radicals deteriorate the body’s immune system
What Are The Best Sources Of Essential Fatty Acids
Fatty acids can be found in lots of plant foods, particularly nuts, seeds and oils. Here are some of the best sources of EFAs.
Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.
































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Comments