Types Of Collagen—Everything You Need To Know Before Buying The Supplement
Last updated on
Chances are you’ve already heard about collagen, a substance that can do wonders for your health—if you take it the right way. But how exactly is “right”? For example, is all collagen equally beneficial, and what are its functions in your body to begin with? What are the types of collagen you need to know about?
Those are some wise questions, and we will answer them all! Let’s take a close look at the 9 most important things to know about collagen before buying (and taking) it to improve your health!
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein that accounts for as much as 35% of ALL protein in the human body, being the primary extracellular “building block.” You can imagine them as tiny ropes with special sites where different molecules can be attached, drastically changing the end structure and function of collagen.
Important Things You Need To Know About Collagen
1. Different Types Of Collagen
The first important thing to know about collagen, is that there are quite a few different types of it: whole 28, to be exact, and they all play different roles in your body. Some of them are better for your skin, others are beneficial for the bones and joints. They all have their peculiarities, so take a moment to get acquainted with the essential ones for your need!
In different forms, collagen is responsible for providing your organs and tissues with the appropriate structure to suit their functions.
For example, fibers of type I collagen are like tiny cross-linked ropes generously saturated with minerals: this is exactly what gives bones their tensile strength (ability to withstand elongation). On the other hand, the fibrillary structure of type II collagen allows it to effectively contain proteoglycans, an important component of cartilage tissue—thus this type of collagen is present in abundance in the joints.
2. Types of Collagen For Specific Needs
The second thing you need to know about collagen is that different types of collagen are better for different tissues and organs in your body.
Here are a few examples:
- Type I collagen—skin, bone, tendons
- Type II collagen—cartilage (joints)
- Type III collagen—reticular fiber (a supportive tissue in such soft organs as liver, bone marrow, lymphatic system, the gut, and many others)
- Type IV collagen—basement membrane, a thin layer which separates the lining of organs from adjacent connective tissue
- Type V collagen—hair, placenta, external surface of all cells.
For skin and beauty (anti-aging), supplementing with Type I collagen can help increase the elasticity of high movement areas of the skin where wrinkles form, such as the forehead, eye region, around the mouth and on the neck. Fortifying the skin’s structurer will help reduce wrinkles, creases, sagging skin, enlarged pores and cellulite.
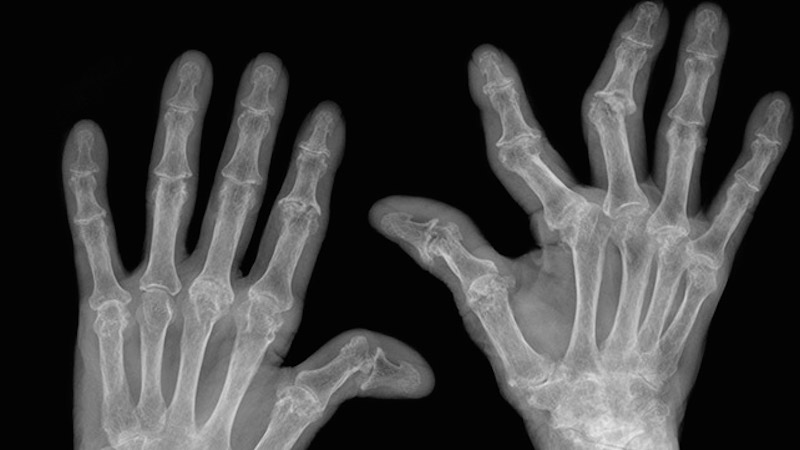
Type II collagen is an effective source for alleviating joint stiffness and increasing mobility. Studies have found that Type II reduces joint pain in arthritis—osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
I can hear you wonder: “So, are you saying that I should look for supplements with specific types of collagen aimed at the organ or tissue I want to support?”
Yes, and no. You see, around 90% of the body’s collagen is composed of the first three types. Although, if you have a very specific need, for example, you have rheumatoid arthritis, then taking a Type II collagen will greatly benefit your body in rebuilding the joints and reducing the pain.
3. Providing Your Body With The Right Building Blocks
The third important thing you need to know about collagen is that it’s formed in your body via “self-assembly” to a great extent. Meaning that, if you have enough “building blocks”, your body will build the types of collagen it most needs. Simple as that!
In other words, your collagen supplement (if you choose it right) will act as these blocks, and your body will do all the rest. Now the question is: what collagen supplements should you look for?
4. Gelatin Vs Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
Basically, the two main types of collagen supplements are gelatin and hydrolyzed collagen peptides (also known as collagen hydrolysate or, rarely, hydrolyzed gelatin). Both have the same exact content of nutrients and roughly the same benefits for your health, but there are a few essential differences.
- Hydrolyzed collagen has higher bioavailability than gelatin, as it comes broken down into smaller fragments. Collagen hydrolysate can be conveniently added in both hot, warm, and cold water, and is much more convenient to take, as you can add it to your juices or smoothie, for example.
- Unlike hydrolyzed collagen, gelatin can be dissolved only in hot water. If you choose to go with gelatin, the only way you’ll be able to take it is, well… Make gelatin with it.
- Although plain gelatin is flavorless, some people may not like its flabby consistency. Hydrolyzed collagen is practically indiscernible in beverages.
Both supplement options are absolutely natural. They are extracted from animal body parts, such as the skin, joints, and bones. The only difference is in the convenience to take, and a little better bioavailability of collagen hydrolysate (about 90% of it are absorbed, versus 85.97% of gelatin) due to the smaller fragments of collagen it contains.
As a result, hydrolyzed collagen peptides are better distributed throughout the body’s tissues, and start imposing their fabulous health benefits a tad faster!
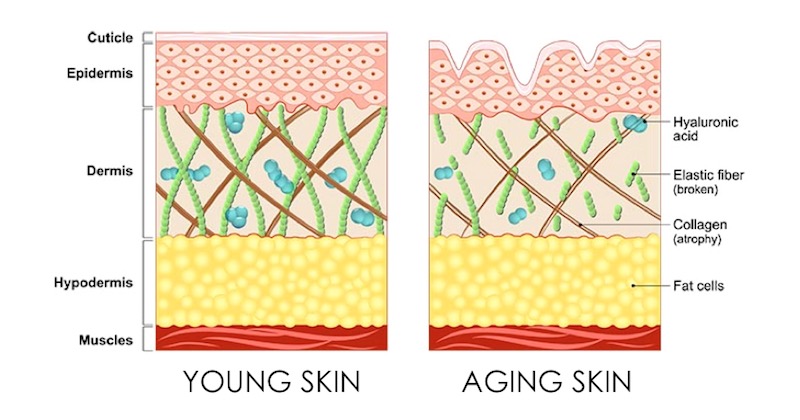
5. Hyaluronic Acid And Collagen
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally-occurring substance found in almost every cell in our body. It is distributed throughout our connective tissue, brain tissue and epithelial tissue that lines our organs, vessels and cavities in the body.
Hyaluronic acid is a hydrating agent that complements and supports collagen, enhancing the body’s ability to produce, synthesize and use collagen much more efficiently.
In joint health, hyaluronic acid works by maintaining the lubrication of joints. It increases the resilience of cartilage by delivering nutrients, removing waste products, replenishing synovial fluid and reducing the effects of friction in the joints.
Hyaluronic acid works with collagen by providing hydration and moisture to the skin, improving elasticity, healing of wounds, tissue repair, dry scalp, and even improve the moisture in our eyes, preventing dry eyes.
If you find a collagen supplement that includes hyaluronic acid as one of its ingredients, it is definitely better for aiding in hydration and regeneration.
6. Collagen for Joint, Bone, and Muscle Health
Perhaps, one of the most well-researched topics in terms of collagen benefits are its effect on the skeletomuscular system health. Let’s take a look at some of the most important of them!
- A 2000 study highlighted that collagen hydrolysate alleviates joint pain in osteoarthritis and improves overall joint health.
- According to a 2008 study, collagen hydrolysate can significantly improve joint pain in athletes who suffer from activity-related joint pain.
- A Japanese 2012 study by Sugihara and coauthors spotlighted that supplementation with hydrolyzed collagen peptides enhances cartilage protection and regeneration.
- In 2013, an animal study showed that hydrolyzed collagen peptides increase bone mass in growing rats, thus indicating that this supplement could be highly beneficial for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis.
- A quite unexpected result was seen in a 2015 study: It showed that collagen hydrolysate supplementation increases muscular strength and helps lose fat in elderly man when combined with resistance training.
Collagen protects your cartilage and helps to regenerate previous damage, supports bone density, and enhances muscle strength.
7. Collagen for Gut Health
Let’s start with the fact that collagen hydrolysates contain a lot of amino acids which are essential for the growth of bifidobacteria, thus making it a powerful prebiotic (a substance or complex of substances that promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria). This means that, although indirectly, collagen hydrolysate might be able to:
- Improve gut health and “patching” up a leaky gut.
- Prevent development of traveler’s diarrhea.
- Prevent development of pouchitis, an inflammation of the artificial rectum in patients after colectomy.
- Reduce symptoms of hay fever (allergic rhinitis).
- Help lower total cholesterol levels, thus helping to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
A few other studies indicate that hydrolyzed collagen peptides could be beneficial for people aiming to control their food intake and lose weight in general, as it can help you stay full for longer, and improve adherence to calorie-restriction diets.
Collagen acts as a powerful prebiotic, normalizes your gut’s microflora, and helps you stay on track of your diet!
8. Collagen for Skin, Hair and Nails
One of the most widespread health claims regarding collagen in general is that it can slow down skin aging and promote the health of your hair and nails. But is that true?
Absolutely! And there are a ton of studies that confirm that! Collagen can drastically improve signs of skin aging, hair and nail health.
For example, in 2014 a study revealed that a daily intake of a supplement made of hydrolyzed collagen and a bit of additional nutrients significantly improved visible signs of skin aging after 60 consecutive days. This includes:
- Skin dryness
- Wrinkles
- Depth of the nasolabial fold
Plus, after 12 weeks, the same study showed an increase in skin collagen density and overall skin firmness. If that’s NOT a fabulous result, I don’t know what is!
Last but not least, hydrolyzed collagen peptides contain amino acids that are essential for the health of hair and nails, enhancing growth and reducing brittleness.
9. Most Effective Bioavailability and Potency
Now let’s have a few words on bioavailability and potency for you to get the most out of your hydrolyzed collagen supplements.
All collagen is derived from animal sources. Depending on the type of collagen you need, the source may play a role in its effectiveness.
For Type I, it is recommended to get your collagen source from fish (marine). Studies show that fish collagen peptides are finer, giving them superior bioavailability to your skin, hair and nail health.
For Type II, it is recommended to get your collagen source from (humanely-raised) chicken that is loaded with joint-healthy condroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate—both of which are excellent for healing your joints.
And for Type III, it is recommended to get your collagen source from grass-fed beef (bovine) found from the cartilage, bones and hides of cows. Bovine collagen is almost identical to human collagen, making it effective and supportive for our connective tissue and internal soft organs.
Although there is no single opinion on how much you should take, most studies with positive results feature a single dose of 7,000 to 10,000 mg per serving daily. Nevertheless, make sure to carefully read the instructions provided by the manufacturer for best results.
And, of course, remember that supplements in liquid form are generally absorbed better than powders or tablets. In other words, if you dissolve a dose of hydrolyzed collagen peptides in a glass of water, you’ll most likely get better results than if you would take roughly the same amount of collagen in powder or gelatin form.
Aim for hydrolyzed collagen, with about 7,000 to 10,000 mg of collagen per serving and take it dissolved in a beverage of your choice.
BUY QUALITY HYDROLYZED COLLAGEN
Last Thoughts Before You Go
In the vast majority of studies that we’ve researched while writing this article, no side effects were observed as a result of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation.
When introducing collagen supplements, make sure to start gradually, giving your body plenty of time to get used to this sudden increase in one specific nutrient. Most likely, if you follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer, you won’t experience any unpleasant effects, but if you know that your guts are prone to throwing a ruckus from time to time—be gentle to it! 🙂
Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.
Comments
Leave a Reply
































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Hi Sara,
I eat a Kosher Diet, is there a Collagen that fulfills that requirement?
Thank You for your website, it’s been extremely helpful to both my husband and I.
Gabbai