What Is A Heart Attack And What Happens During A Heart Attack
Last updated on
A heart attack can strike suddenly. Its symptoms are quite common, and many people don’t initially realize that they’re already having one. At times, there may be only ONE symptom and this makes the heart attack even more difficult to diagnose.
But what really happens when you have a heart attack? Read on to find out more.
What Is A Heart Attack?
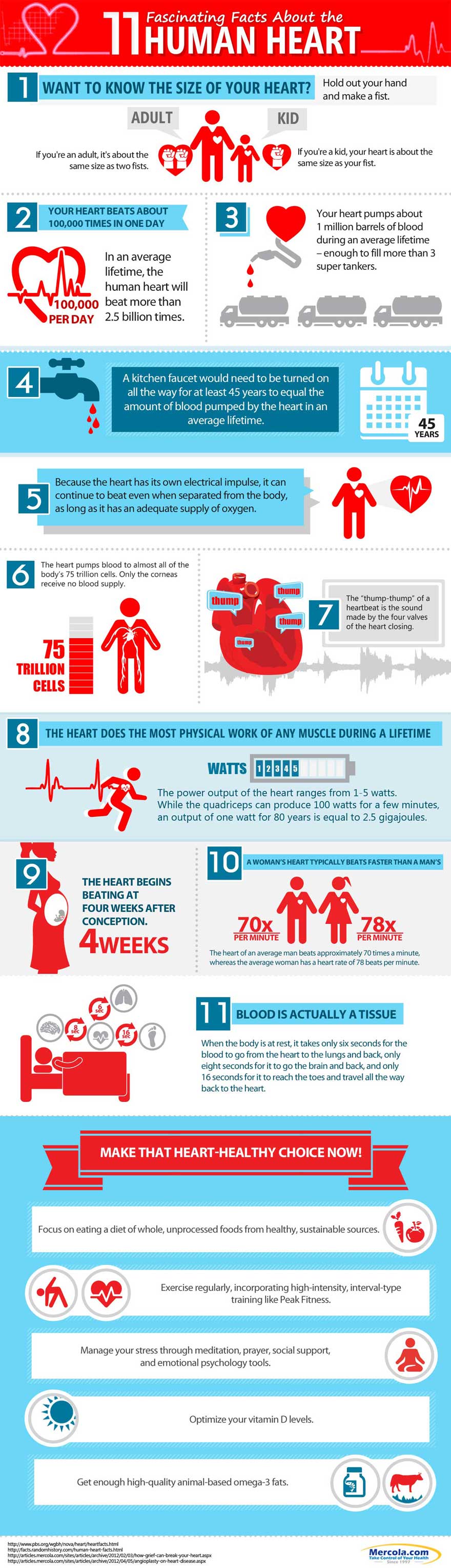
The heart is an extraordinary organ that can still function even when detached from your body, as long as it has an adequate supply of oxygen.1 It must work relentlessly to pump blood throughout your body.
11 Fascinating Facts About The Human Heart
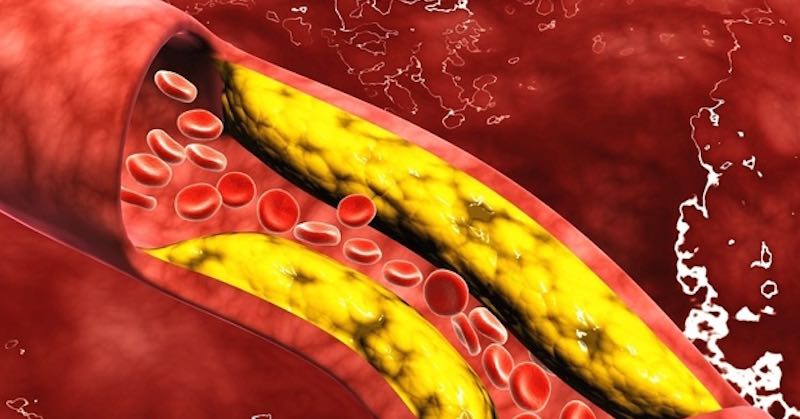
It’s vital that your heart receives ample oxygenated blood and the heart muscle can die if it receives an insufficient amount. The loss of blood supply may occur when plaque builds up in your coronary arteries and blocks the blood’s flow to your heart. Plaque is made up of cholesterol, fatty substances, cellular waste, calcium, and fibrin.
When plaque builds up in your coronary arteries, it can result in coronary artery spasm or atherosclerosis, which is the tightening or hardening of heart muscles and can lead to a blood clot when the plaque ruptures.2,3 Atherosclerosis can lead to coronary heart disease, which can trigger a heart attack.4
According to the American Heart Association, a heart attack can also occur when the blood supply cannot reach the heart due to narrowed heart arteries, commonly known as ischemic heart disease.5
An Unconventional Perspective on Heart Attack
In an article published last December 2014, I featured Dr. Thomas S. Cowan who gave us a different perspective on how heart attacks occur. He said that a heart attack occurs not because your coronary arteries are blocked, but rather it is caused by an imbalance in the parasympathetic and sympathetic sections of your central nervous system.
Stress is a major reason for the imbalance in your central nervous system. When you experience chronic stress, an emotional sensor will activate your sympathetic nervous system. When your parasympathetic nervous system does not compensate for it, this will result in an unexpected release of adrenalin, a hormone that breaks down the myocardial cells, affecting the blood flow needed by your heart. Hence, a heart attack occurs.
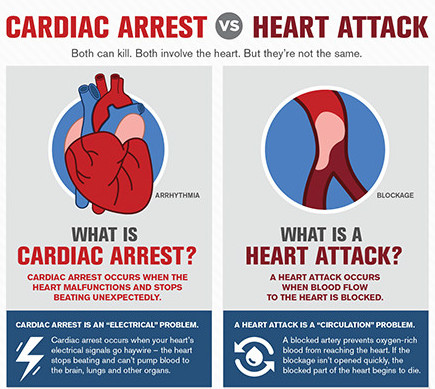
Heart Attack Vs. Cardiac Arrest
It is important to know the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest since people are often under the mistaken impression that they are the same. Cardiac arrest happens due to the electrical malfunction of your heart, which causes an irregular heartbeat and usually occur without any warning.
Cardiac arrest is caused by different health reasons like cardiomyopathy or thickened heart muscle, heart failure, arrhythmias, long Q-T syndrome, and ventricular fibrillation. A heart attack may increase the risk of having a cardiac arrest, and is the common reason for its occurrence.6
Related Article: How to tell you’re at risk of a heart attack and steps to prevent it.
What Happens During A Heart Attack?
Ever wondered what happens during a heart attack? Let’s dig deeper into what really goes on inside your body during a heart attack, and the role that plaque plays in this fatal condition.
If your heart has been accumulating plaque over the years, it can thicken enough to obstruct your blood flow. You might not readily notice that you already have a narrowed blood flow, because once a coronary artery becomes incapable of bringing blood to your heart, other coronary arteries expand to take care of the incapacitated artery’s job.
Plaque is covered in a solid fibrous cap on the outside but its inside is soft due to its fatty contents.7 If the plaque in your coronary artery is ruptured, the fatty substances become exposed. Platelets rush to the plaque, forming a blood clot (the same thing that happens when you get a cut or any laceration).
The blood clot formed becomes the main obstruction to your blood flow. Your heart becomes starved of oxygen-rich blood, and your nervous system immediately sends signal to your brain about what’s going on. You will start sweating and your heart rate will speed up. You will also feel nauseous and weak.
As your nervous system sends signals to your spinal cord, your other body parts start to ache. You will start feeling an immense chest pain that slowly crawls to your neck, jaw, ears, arms, wrists, shoulder blades, back, and even in your abdomen. Heart attack patients say that the pain they experienced was like a clamp squeezing their chest, and may last from several minutes to many hours.
Your heart’s tissues will die if you’re not given proper treatment right away. If your heart has stopped beating completely, your brain cells will die in a span of just three to seven minutes. If you are treated immediately, your heart will start to heal but the damaged tissue will never work again resulting in a permanent slow blood flow.8
Related Article: How to tell you’re at risk of a heart attack and steps to prevent it.
This article was originally published on Mercola.com. It is republished here with permission.
Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.
































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Comments