How To Fix Chronic Inflammation By Tweaking Your Omega Fatty Acids Ratio
Last updated on
Fish oil is often touted as the best source of omega fatty acids (and the most affordable too).
Now, while everyone knows that omega fatty acids (like omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9) are a good thing, almost nobody knows exactly what they mean.
Are omegas really good for you? Should you focus on the 3s or the 6s?
Is it true you can fix chronic inflammation by tweaking your ratio of omegas?
Let’s dig into the matter one question at a time.
What Are Omega Fatty Acids?
All omegas are unsaturated fatty acids. Of the three most commonly mentioned omegas – 3, 6, and 9 – your body can produce only omega-9s. For good health, you have to get enough omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from dietary sources, and that’s why they’re called essential fatty acids.
Keeping an eye on your fatty acid intake (as well as the ratio between specific types of fatty acids in your diet) is key for reaching optimal body composition, maximizing physical performance, and even keeping your brain function sharp through the years.
How Do The Omega Fatty Acids Work?
How Dietary Omegas Work
All the cell membranes in your body contain an omega-6 known as arachidonic acid (ARA).
When your cells are damaged in any way, the ARA in the cell membranes is released and metabolized by cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes into all sorts of inflammatory molecules (eicosanoids).
These inflammatory molecules aren’t exactly a bad thing—you need them to fight off viruses, combat bacterial threats, support your immune system, and even kill cancer cells. That’s why producing these eicosanoids when your cells are damaged is actually a good idea.
The problem is that all sorts of environmental factors (air and water pollution, chemicals in food, artificial dyes, etc.) can activate ARA release and eicosanoid production even where there is no cell damage yet.
Ironically, these inflammatory molecules then cause cell damage and lead to even more eicosanoids being produced, and this cycle empowers itself into chronic inflammation.

How To Prevent Inflammation with Omega-3
So how can you prevent this excess production of inflammatory molecules when you don’t need them?
Get some omega-3s!
Roughly speaking, your body uses omega-6s to produce pro-inflammatory molecules and omega-3s to create anti-inflammatory molecules – through the same enzymes!
In other words, when you get a lot of omega-3s, you’ll be limiting your body’s ability to process omega-6s into inflammatory stuff.
To summarize:
- You need omega-6s to support the immune system and fight external threats (infections, chemical damage, etc.)
- You need omega-3s to prevent excessive and spontaneous inflammation, as well as promote regeneration
As to omega-9s, they aren’t really a problem. Contrary to the previous two classes of omegas, your body can produce omega-9s just fine. You’ll have to get your 3s and 6s from the right foods and in the right amount.
But why should you bother?
Let’s take a good look at all the confirmed health benefits of the essential omegas.
Health Benefits of the Omega Fatty Acids
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Common types of omega-3s: Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) in plant oils, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexanoic acid (DHA) in seafood.
Health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids:
- The omega-3s in fish oil have been confirmed to lower blood pressure, improve blood lipids, and promote the health of the arteries—all of these effects are essential for preventing cardiovascular disease.
- Regular omega-3 intake may both prevent and effectively treat existing depression.
- The DHA in seafood may prevent age-related macular degeneration, which is the most common reason of worsening eyesight in the elderly.
- Getting enough omega-3s has been linked to better bone and muscle health in adults.
- Fish oil supplements rich in omega-3s have been confirmed to improve metabolic health, reduce body fat, and decrease cardiovascular risk.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Common types of omega-6s: linoleic acid (LA), calendic acid, gamma-linolenic acid (GLA).
Health benefits of omega-6 fatty acids:
- Long-term GLA intake has been linked to reduced nerve pain in cases of diabetes complications like diabetic neuropathy, which is damage to the nerves by high blood sugar.
- In moderate amounts, linoleic acid has been reported to treat autoimmune disorders BUT the same reports highlighted that LA can worsen them when taken excessively.
- Gamma-linolenic acid is a major regulator of immune response. When taken in the right amounts, it has anti-inflammatory properties (despite being and omega-6).
- In cases of physical damage (wounds, for example), pro-inflammatory omega-6s like oleic and linoleic acid have been confirmed to speed up the healing.
Tweaking Your Omega Fatty Acids Ratio
For thousands of years, humans lived on something close to a 1:1 ratio of essential omegas, meaning they ate as much omega-6 fatty acids as omega-3s.
Ancient hunter-gatherer civilizations had a 4:1 to 1:3 ratio of omega-6s to omega-3s.
Then, as the centuries went by, this ratio shifted towards omega-6s, and now the typical Western diet features 15-17 times more omega-6 than omega-3 fatty acids.
Imagine the storm of inflammatory molecules your body is producing from such an abundance of omega-6 fats!
Studies indicate that by adopting a ratio close to 4:1 (the one we had for centuries) or lower, it’s possible to:
- Decrease cardiovascular risk and total mortality by up to 70%
- Lower breast cancer risk in women
- Soothe chronic inflammation, like during rheumatoid arthritis
- Reduce colorectal cancer growth (2.5:1 ratio of omegas 6:3)
In other words, although you need both types of essential omegas in your diet, their ratio is much more important for your general health. Aim to get more omega-3s and control your intake of omega-6.
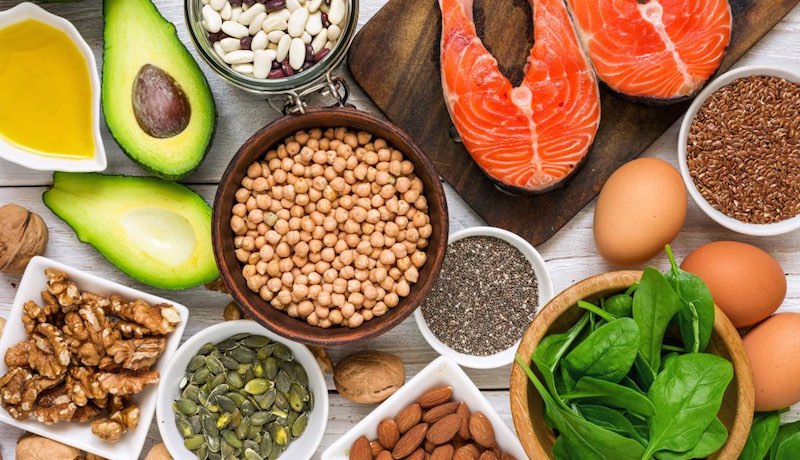

Food Sources of Omega-6:
Eat less of these omega-6 food sources (according to the National Cancer Institute):
- Poultry
- Eggs
- Vegetable oils
- Cereals
- Chips
- Pizza
- Processed meat
Food Sources of Omega-3:
Eat more of these omega-3 food sources:
- Fish and seafood are the best source of all omega 3s, particularly cold-water fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, and herring. Be careful with certain ones – read about tilapia and why you should never eat tilapia that is farm bread
- Flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts
- Omega-3 fortified foods
Of course, taking fish oil supplements is the easiest (and cheapest) way of getting enough omega-3s to maintain a healthy ratio of omegas and reap all the amazing benefits listed above. I highly recommend this fish oil supplement from Dr Tobias.
The Bottom Line
At first sight, the matter of omega fatty acids in your diet seems complex and way too science-like—because it is! But if you want it boiled down to a few sentences, here it goes:
- For optimal health, you have to eat 4 times more omega-6 fatty acids than omega-3 fatty acids (have a ratio of 4:1 omega-6 to omega-3 respectively).
- The average Westerner eats 16 times more omega-6s than omega-3s, which leads to chronic inflammation and all sorts of diseases.
- To fix your ratio, control your intake of omega-6 sources (poultry, eggs, vegetable oils, cereals, processed foods) and eat more omega-3 sources (fish, flaxseed, walnuts, fortified foods).
- The easiest way to ramp up your omega-3 intake is to take a fish oil supplement.
Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.
Comments
Leave a Reply































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Thanks Sara, your blog has helped me immensely.
One question what do you know about AVM MALFORMATION and what do you recommend I do to alleviate my concern? Thanks I look forward to your advice.