Sesame Seeds: Its Cancer Inhibition Properties Plus Other Health Benefits
Last updated on
Sesame (Sesamum indicum) is believed to be one of the first plants domesticated by man: archeological findings go way back to at least some 4000 years ago! Initially cultivated in India, this wondrous plant has quickly spread around the world to be used in dozens of different ways.
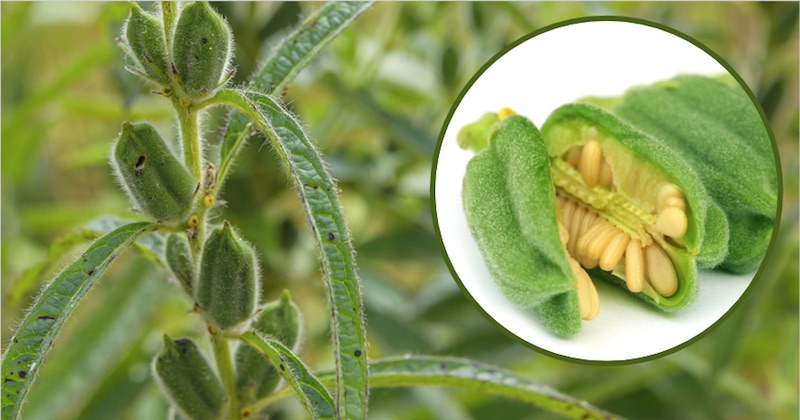

Throughout the millennia, sesame seeds and oil were a staple ingredient in Babylonian magic rituals, ancient Egyptian medicine, classic European cuisine, and even burned as a light source in China. Today, we know it mostly as a topping for buns.
In terms of nutrition, sesame seeds come jam-packed with minerals (calcium, copper, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and iron), vitamins (B1, B6), dietary fiber, and healthy fat.
However, the real value of sesame seeds isn’t in straightforward nutrition: it’s the special compounds present in them, like lignans and sesamin.
Sesame seeds in curbing cancer growth: How real?
According to a 2011 study, sesamin is able to manage the growth of several common types of cancer including colon, breast, pancreas, lung, and leukemia.
The extensive research into sesamin’s anti-cancer properties also indicates that it could be a possible adjuvant therapeutic agent for the prevention and treatment of various types of cancer, thanks to its multi-targeted approach to disrupting cancer cell processes.
But the health benefits that we can derive from sesame seeds are not just limited to potentially inhibiting cancer growth, sesame seeds can actually be the source of some seriously amazing health benefits too.
Let’s take a good look at the most important of them.
Health Benefits of Sesame Seeds
Reduce cholesterol absorption
According to a study from 2005, sesame seeds are the richest source of phytosterols (400-413 mg per 100 g) among all seeds commonly eaten in the US. Why’s that important?
Several studies have confirmed that a moderate to high daily intake of phytosterols significantly reduces low-density lipoprotein (LDP) cholesterol levels in a dose-dependent fashion!
It’s recommended to aim for at least 459 mg/day of phytosterols as this is the level at which cholesterol absorption in the guts is significantly reduced.
Potentially reduce blood pressure and cardiovascular risk
The main lignan (a class of polyphenols) in sesame seeds is sesamin, and it has some beneficial properties.
For instance, a Japanese study from 2009 reported that daily supplementation of 60 mg sesamin was able to modestly decrease systolic blood pressure by 3.5 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 1.9 mm Hg on average.
The study also noted that a reduction of 2-3 mm Hg in blood pressure is enough to possibly reduce cardiovascular disease rate, so snacking on some sesame seeds daily may be meaningful to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases!

Soothe inflammation
A daily dose of 40 mg of sesame seeds over the course of 2 months was able to significantly reduce inflammation in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Most likely, this effect is based on the outstanding antioxidative properties of sesame oil and its phytosterols.
Protect the brain from poor oxygen supply
There is evidence from animal studies that sesamin and sesamolin, two lignans from sesame oil, are able to reduce brain damage from ischemia (poor blood and oxygen supply) by approximately 50%.
Although further human studies are needed to make solid recommendations on this matter, the potential of these compounds is promising.
Boost the antioxidant potential of vitamin E
A study shows that lignans in sesame seeds can help protect our body’s cells from damage, especially when they boost the antioxidant activity of vitamin E. This can contribute in preventing various diseases related to oxidative stress and cell damage.
Help prevent the formation of blood clots
Sesamol, another lignan in sesame seeds, has been confirmed to have anti-thrombotic properties, meaning it can prevent the formation of blood clots and arterial plaque. Sesamolin and sesamin showed similar potential but somewhat milder.
Lower fasting blood glucose levels
Using sesame oil every day in place of your regular cooking oil significantly improves fasting glucose levels, according to a 2008 study.
Subjects received 30 g/day sesame oil for 6 weeks. Patients were instructed to use sesame oil in place of other cooking oils for 42 days.
Adding this oil in your dishes might be a beneficial addition to diabetes management strategies.
Reduce muscle damage, improve physical performance in athletes
A study from 2017 reported that taking just 40g (two tablespoons) of sesame seeds per day was able to effectively reduce muscle damage in athletes and improve their aerobic capacity, meaning the body’s ability to capture and use oxygen to fuel physical activity.
Although most people won’t be able to actually feel this effect, this suggests that sesame seeds might be a beneficial addition to an athlete’s diet to help cope with the demands of intense sports training.
Possible treatment for women with oligomenorrhea
Oligomenorrhea is the medical term for having abnormally infrequent menstruations (with more than 35 days between the periods).
In 2014, a result from a pilot study in Iran, where sesame seeds are an important herb in their traditional medicine, reported that taking sesame seeds daily for seven days was able to effectively restore regular periods in about 80% of women with no side effects.
Although, stronger clinical trials with control group are recommended to strengthen this hypothesis.
Improve the function of the endothelium (lining of the blood vessels)
A study explored how sesame oil affects blood vessel health (endothelial function) in men with high blood pressure.
After consuming 35 grams of sesame oil every day for two months, it was observed that the endothelial function of the participants showed significant improvement.
For instance, a healthy endothelium is able to produce nitric oxide (NO) in sufficient amounts. Nitric oxide is the body’s primary way to widen up the blood vessels—meaning lower blood pressure, better blood and oxygen supply, and lower risk of cardiovascular events.
The Bottom Line
Considering all the health benefits that sesame seeds have to offer, they are seriously underrated and underused.
Of course, eating some 100 g of actual sesame seeds daily may be tricky for some people, so consider the option of going for just a couple tablespoons of sesame oil—that will be enough!
Important! For optimum results, use sesame oil fresh, or in very low to medium heat. Do not use in high heat cooking.
No matter which approach you choose, remember that sesame seeds are worth so much more of your attention than being a pleasant bonus to your hamburger buns.
Sprinkle them over salads and juices, bake some healthy cookies, add them to your morning cereals: the options are endless, and all of them will be extremely beneficial for your health!
Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Comments