Deadly Fungus That ‘Eats You From the Inside Out’ Invades Us: ‘Hundreds of Thousands of Lives at Risk’
Last updated on
Imagine breathing in tiny, invisible particles every day without even knowing it. For most of us, these microscopic spores pass through our lungs unnoticed, doing no harm. But for some, these same spores are a silent killer, capable of attacking the body from the inside out, slowly rotting tissue and causing organ failure. This is the reality of Aspergillus fumigatus, a deadly airborne fungus that is quietly spreading across the United States. Unlike the dramatic, world-ending scenarios often depicted in movies or video games, this threat is very real, and it’s here. With rising global temperatures and increasingly humid conditions, the conditions are ripe for this fungus to flourish in the warmest, dampest parts of the country. Florida, Louisiana, Texas, Georgia, and California are seeing the worst of it, but the risk is spreading, especially in areas with aging infrastructure and crowded cities. What makes this threat so alarming is not just its ability to infect vulnerable individuals, but its potential to evade treatment. As drug-resistant strains of the fungus become more common, medical experts warn that the current response may be inadequate, putting hundreds of thousands of lives at risk. In a world already grappling with the effects of climate change, this silent epidemic may be one of the most underestimated dangers we face. So, how do we respond to a microscopic invader that can strike without warning? And more importantly, what can we do to protect ourselves and those we care about from a fungus that may be growing in the air we breathe? The time to find answers is now, before it’s too late.What is Aspergillus Fumigatus?
Aspergillus fumigatus is a type of mold that thrives in the environment, invisible to the naked eye but incredibly persistent. Its tiny spores, called conidia, are carried effortlessly by the wind, floating through the air and infiltrating homes, hospitals, and even agricultural fields. These spores are so minuscule that most people breathe them in without even realizing it—every day, potentially without consequence. But for some, these invisible invaders can be deadly. This fungus is found in soil, decaying plant matter, and even indoor dust, making it nearly impossible to avoid. It thrives in warm, damp conditions, which makes places like compost piles, humidifiers, and poorly ventilated buildings ideal breeding grounds. In fact, Aspergillus fumigatus can survive in temperatures over 120 degrees Fahrenheit, which is why it’s often found in agricultural settings where such conditions are common, especially in places that experience prolonged periods of heat. For the majority of people with healthy immune systems, the spores cause no harm. The body’s natural defenses fight off the fungus before it can settle in the lungs or other parts of the body. However, for those with weakened immune systems—such as cancer patients, people with HIV, or those recovering from serious infections like influenza—this fungus becomes a serious threat. It can trigger an aggressive infection known as aspergillosis, which can cause devastating damage to the lungs and, in severe cases, spread to other organs such as the brain, heart, and kidneys. Unlike some infections, aspergillosis doesn’t always show immediate symptoms, which can delay diagnosis and treatment. In many cases, it starts as a chronic condition, where the infection persists and slowly worsens, causing long-term lung damage. For the most vulnerable individuals, invasive aspergillosis can be fatal.From Lung Infections to Organ Failure

Which States and Cities are Affected?
The Role of Climate Change in Fungus Spread

The Growing Threat of Drug Resistance
Prevention and Precautionary Measures

The Importance of Monitoring and Research
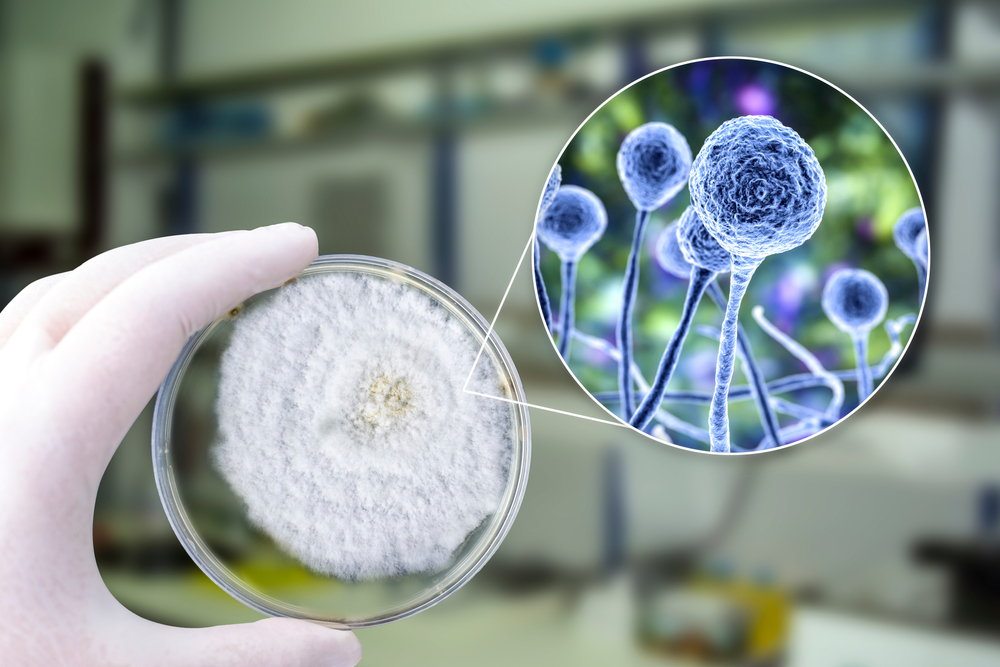
Why We Should Care

A Wake-Up Call for the Future
The rise of Aspergillus fumigatus as a public health threat is not a fluke—it is a clear and pressing signal of the changing world we live in. As temperatures rise, ecosystems shift, and drug resistance accelerates, we are witnessing the conditions that allow an environmental fungus to become a lethal, treatment-resistant pathogen. This is not just a story about a single fungus. It’s a warning about the cascading consequences of climate change, unchecked agricultural practices, underfunded medical research, and the growing blind spots in public health infrastructure. When fungal infections that were once rare begin to cause widespread illness and death, and when standard treatments begin to fail, we are no longer dealing with isolated incidents—we are facing a systemic risk. But the future is not fixed. Coordinated action today can blunt the impact of this threat. That means investing in antifungal drug development, updating agricultural policies, improving indoor air quality, tracking fungal infections more rigorously, and educating the public and healthcare workers alike. It also means addressing climate change with the urgency it demands—because the warmer our planet gets, the more favorable the conditions become for pathogens like Aspergillus fumigatus to thrive. In a world hyper-focused on viruses and bacteria, fungal diseases remain dangerously underestimated. Yet they are growing stronger in silence. This is our opportunity to catch up—to treat the microscopic world with the seriousness it deserves, before a once-manageable fungus evolves into something far more devastating. The window for preparedness is still open, but not indefinitely. Now is the time to act.Some of the links I post on this site are affiliate links. If you go through them to make a purchase, I will earn a small commission (at no additional cost to you). However, note that I’m recommending these products because of their quality and that I have good experience using them, not because of the commission to be made.
































 JOIN OVER
JOIN OVER
Comments